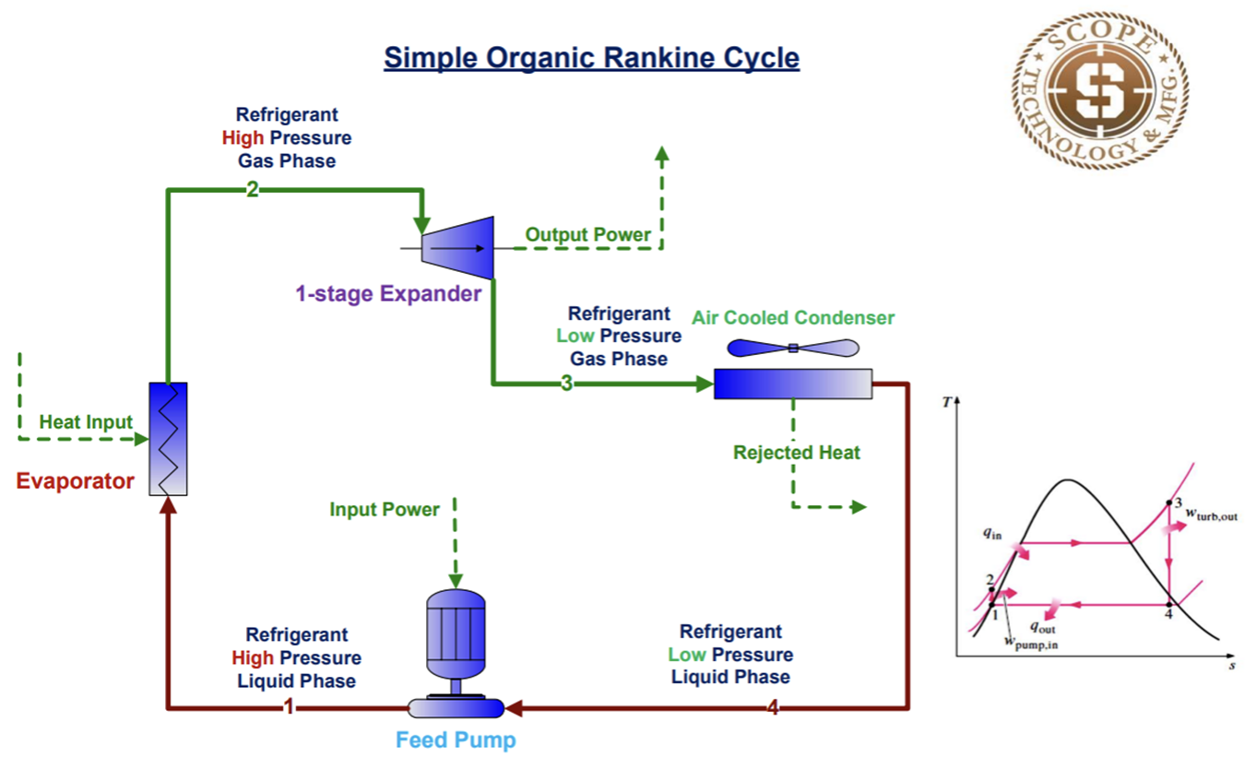
Impact of Ambient Temperature on Heat Source Selection in Organic Rankine Cycle (O.R.C.) Systems
In the realm of power generation through waste heat recovery, geothermal, microgrids, combined heat and power (CHP), and oil and gas applications, the selection of a suitable heat source is paramount to the efficiency and overall performance of an Organic Rankine Cycle (O.R.C.) system. As we delve into the intricate world of O.R.C. systems, it becomes evident that the ambient temperature plays a pivotal role in determining the cooling cycle and efficiency of these units. Understanding how ambient temperature influences heat source selection, output impacts, and strategies to mitigate negative effects while enhancing positive outcomes is crucial for engineers, technical professionals, and procurement audiences involved in manufacturing and prototyping O.R.C. units.
The Interplay Between Ambient Temperature and O.R.C. Systems
Impact of Ambient Temperature on Cooling Cycle Efficiency
The efficiency of an O.R.C. system is intricately linked to the ambient temperature in which it operates. Higher ambient temperatures tend to reduce the temperature differential between the heat source and the cooling medium, thereby affecting the cycle efficiency. This reduction in temperature differential can lead to decreased power output and efficiency of the O.R.C. system. Conversely, lower ambient temperatures can enhance the temperature differential, potentially boosting the system’s efficiency.
Various Impacts on Output
- Power Output: High ambient temperatures can negatively impact the power output of an O.R.C. system by reducing the temperature gradient available for power generation. This can result in lower electricity generation capacity and efficiency.
- System Performance: Ambient temperature variations can influence the overall performance of the O.R.C. system, affecting parameters such as the heat transfer rate, fluid properties, and compressor efficiency. These changes can directly impact the system’s reliability and operational stability.
- Component Lifespan: Extreme ambient temperatures can accelerate the degradation of system components, leading to a shorter lifespan and increased maintenance requirements. Proper heat source selection is crucial to mitigate these effects and ensure the longevity of the O.R.C. unit.
Minimizing Negative Impacts and Amplifying Positive Impacts
- Heat Source Selection: Choosing the right heat source is critical in mitigating the negative impacts of ambient temperature on O.R.C. systems. Opting for a heat source with a consistent temperature profile, such as geothermal sources or waste heat from industrial processes, can help stabilize the system performance across varying ambient conditions.
- Thermal Management Strategies: Implementing robust thermal management strategies, such as heat exchangers, thermal storage systems, and insulation techniques, can minimize the influence of ambient temperature fluctuations on the O.R.C. cycle. These strategies help maintain optimal operating conditions and enhance the system’s overall efficiency.
- Advanced Control Systems: Incorporating advanced control systems that dynamically adjust the operating parameters based on ambient temperature variations can optimize the O.R.C. system’s performance. Adaptive controls can ensure efficient operation under varying environmental conditions, maximizing output and efficiency.
Bridging to Future Topics
Understanding the nuances of heat source selection in O.R.C. systems lays the foundation for exploring advanced topics in thermal management strategies for cooling and enhancing O.R.C. performance in diverse environmental conditions. By comprehensively addressing the impact of ambient temperature on O.R.C. efficiency, we pave the way for a deeper dive into optimizing system performance and energy generation across different applications.
In our upcoming discussions, we will delve into thermal management strategies tailored to O.R.C. cooling, focusing on innovative approaches to enhance system efficiency and reliability. By connecting these topics seamlessly, we aim to equip engineers and technical professionals with the knowledge and insights necessary to excel in the realm of O.R.C. system design and implementation.
Through a holistic exploration of heat source selection, system performance impacts, and mitigation strategies, we empower stakeholders in the O.R.C. industry to make informed decisions that optimize energy generation, reduce operational costs, and contribute to sustainable power solutions.
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between ambient temperature and heat source selection in O.R.C. systems underscores the critical importance of understanding these dynamics for achieving optimal performance and efficiency. By delving into the depths of this subject, we pave the way for a more profound exploration of O.R.C. technology and its applications across diverse energy sectors.
As we continue our journey through the realm of O.R.C. systems, let us unravel the complexities, embrace the challenges, and harness the opportunities that lie ahead, driving innovation and sustainability in power generation.