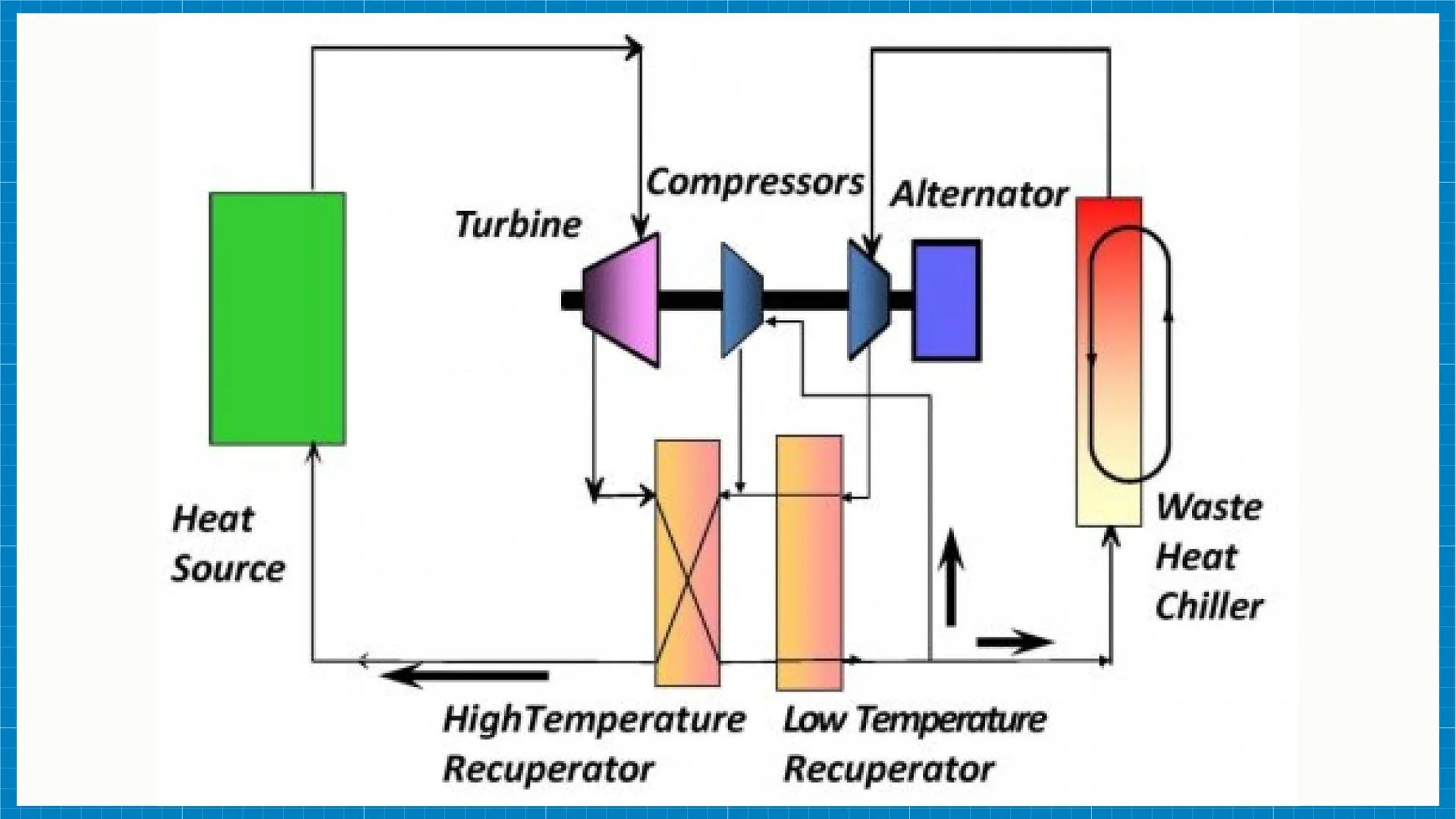
In the realm of Organic Rankine Cycle (O.R.C.) systems, the efficiency and performance of the cycle are intricately linked to the ambient temperature in which the system operates. As we delve into the realm of thermal management strategies for O.R.C. cooling, we are met with a crucial juncture where the impact of ambient temperature on the cooling cycle and overall efficiency of an O.R.C. unit comes to the forefront. This exploration is not just a theoretical exercise but a practical necessity for professionals like you, deeply involved in the manufacturing and prototyping of O.R.C. units for diverse applications ranging from waste heat recovery to geothermal energy, microgrid implementations, combined heat and power (CHP) setups, and oil and gas operations.
Understanding the Influence of Ambient Temperature on O.R.C. Cooling Efficiency
Impact of Ambient Temperature Differentials on O.R.C. Efficiency
The efficiency of an O.R.C. cycle is significantly influenced by the ambient temperature differentials it encounters. Higher temperature differentials can enhance the cycle’s efficiency by allowing for increased heat transfer rates and improved power generation. However, high temperatures can also lead to operational challenges such as increased thermal stresses on system components and potential performance degradation over time. On the other hand, lower temperature differentials may reduce the efficiency of the cycle, affecting power output and overall system performance.
Effects on Output: Minimizing Negative Impacts and Amplifying Positive Impacts
Minimizing Negative Impacts
- Heat Exchanger Design: Optimal heat exchanger design is crucial to minimize the negative impacts of ambient temperature variations. Efficient heat exchangers can help maintain thermal stability within the system, ensuring consistent performance regardless of external temperature fluctuations.
- Cooling System Optimization: Implementing advanced cooling systems can mitigate the adverse effects of high ambient temperatures on O.R.C. units. By regulating the temperature within the system, cooling systems can safeguard components from overheating and prevent performance degradation.
- Insulation and Enclosure Strategies: Utilizing effective insulation and enclosure strategies can protect the O.R.C. unit from external temperature influences, maintaining a stable operating environment and preventing energy losses due to ambient heat exchange.
Amplifying Positive Impacts
- Thermal Energy Storage: Integrating thermal energy storage systems can capitalize on favorable ambient temperatures by storing excess heat for later use. This approach can enhance the overall efficiency of the O.R.C. cycle by optimizing heat utilization and power generation during peak operating conditions.
- Adaptive Control Systems: Implementing adaptive control systems that can dynamically adjust operating parameters based on ambient temperature fluctuations can maximize the positive impacts of temperature differentials. By optimizing system settings in real-time, adaptive controls ensure efficient performance under varying environmental conditions.
Bridging to Future Topics: Heat Source Selection in O.R.C. Systems
As we navigate the intricate landscape of thermal management strategies for O.R.C. cooling, it becomes evident that the choice of heat source plays a pivotal role in determining the overall efficiency and performance of the system. In the upcoming exploration on “Heat Source Selection in O.R.C. Systems,” we will delve into the diverse range of heat sources available for O.R.C. units, ranging from waste heat streams to geothermal reservoirs, and analyze how these sources impact system efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the optimization of thermal management strategies for O.R.C. cooling is a multifaceted endeavor that demands a nuanced understanding of ambient temperature dynamics and their influence on system efficiency. By strategically minimizing negative impacts and amplifying positive effects through innovative design approaches and control systems, engineers and technical professionals can elevate the performance of O.R.C. units across a spectrum of operational environments. This journey into the realm of thermal management not only enhances our comprehension of O.R.C. systems but also sets the stage for further exploration into critical topics shaping the future of sustainable power generation and energy utilization.